Muslims also believe that Islam is the
original, complete and universal version of a primordial faith that was revealed many times before through
prophets including
Adam,
Noah,
Abraham,
Moses, and
Jesus.
[14][15][16] As for the Quran, Muslims consider it to be the unaltered and final revelation of God.
[17] Religious concepts and practices include the
five pillars of Islam, which are obligatory acts of worship, and following
Islamic law, which touches on virtually every aspect of life and society, from
banking and
welfare to
women and the
environment.
[18][19] Certain religious rites and customs are observed by the Muslims in their family and social life, while social responsibilities to parents, relatives, and neighbors have also been defined. Besides, the Quran and the
sunnah of Muhammad prescribe a comprehensive body of moral guidelines for Muslims to be followed in their personal, social, political, and religious life.
Etymology and meaning
Islam is a verbal noun originating from the
triliteral root s-l-m which forms a large class of words mostly relating to concepts of wholeness, submission, safeness and peace.
[33] In a religious context it means "voluntary submission to God".
[34][35] Islām is the verbal noun of
Form IV of the root, and means "submission" or "surrender".
Muslim, the word for an adherent of Islam, is the
active participle of the same verb form, and means "one who submits" or "one who surrenders". The word sometimes has distinct connotations in its various occurrences in the
Quran. In some verses, there is stress on the quality of Islam as an internal state: "Whomsoever God desires to guide, He opens his heart to Islam."
[36] Other verses connect
Islām and
dīn (usually translated as "religion"): "Today, I have perfected your religion (
dīn) for you; I have completed My blessing upon you; I have approved Islam for your religion."
[37] Still others describe Islam as an action of returning to God—more than just a verbal affirmation of faith.
[38] In the
Hadith of Gabriel,
islām is presented as one part of a triad that also includes
imān (faith), and
ihsān (excellence).
[39][40]
Islam was historically called
Muhammadanism in
Anglophone societies. This term has fallen out of use and is sometimes said to be
offensive because it suggests that a human being rather than God is central to Muslims' religion, parallel to Jesus Christ in
Christianity. Some authors, however, continue to use the term
Muhammadanism as a
technical term for the religious system as opposed to the
theological concept of Islam that exists within that system.
[41]
Articles of faith
| Part of a series on |
| Islam and Iman |
|---|
|
|
| Individuals |
|---|
|
|
| Groups |
|---|
|
|
| Terms |
|---|
|
|
|
|
Concept of God
Islam is often seen as having the simplest doctrines of the major religions.
[3] Its most fundamental concept is a rigorous monotheism, called
tawḥīd (
Arabic:
توحيد). God is described in chapter 112 of the Quran as: "Say, He is God, the One and Only; God, the Eternal, Absolute; He begetteth not, nor is He begotten; And there is none like unto Him" (
112:1-4).
[42] Muslims repudiate
polytheism and
idolatry, called
Shirk, and reject the Christian doctrine of the
Trinity and divinity of
Jesus. In Islam, God is beyond all comprehension and Muslims are not expected to visualize God.
[43][44][45][46] God is described and referred to by certain names or attributes, the most common being
Al-Rahmān, meaning "The Compassionate" and
Al-Rahīm, meaning "The Merciful" (See
Names of God in Islam).
[47]
Muslims believe that the creation of everything in the universe was brought into being by God's sheer command, "'Be' and so it is,"
[48]and that the
purpose of existence is to worship God.
[49] He is viewed as a personal god who responds whenever a person in need or distress calls him.
[50] There are no intermediaries, such as
clergy, to contact God who states, "I am nearer to him than (his)
jugular vein."
[51] God consciousness is referred to as
Taqwa.
Allāh is the term with no
plural or
gender used by Muslims and Arabic-speaking Christians and Jews to reference God, while
ʾilāh (
Arabic:
إله) is the term used for a deity or a god in general.
[52] Other non-Arab Muslims might use different names as much as Allah, for instance "Tanrı" in
Turkish, "Khodā" in
Persian or
Ḵẖudā in
Urdu.
Angels
Belief in
angels is fundamental to the faith of Islam. The Arabic word for angel (
Arabic:
ملك
malak) means "
messenger", like its counterparts in
Hebrew (
malʾákh) and
Greek (
angelos). According to the
Quran,
angels do not possess
free will, and therefore worship and obey
God in total obedience. Angels' duties include communicating
revelations from God, glorifying God, recording every person's actions, and taking a person's
soul at the time of death. Muslims believe that angels are made of light. They are described as "messengers with wings—two, or three, or four (pairs): He [God] adds to Creation as He pleases..."
[53] Some scholars have emphasized a metaphorical reinterpretation of the concept of angels.
[54] Pictorial depictions of angels are generally avoided in Islamic Art, as the idea of giving form to anything immaterial is not accepted.
[55] Muslims therefore do not generally share the perceptions of angelic pictorial depictions, such as those found in Western Art.
Additionally, another kind of being that is sapient in Islam is called
Jinn, who are believed to be invisible to humans and include
Satan.
Revelations

11th-century Quranic manuscript with vocalization marks.
The Islamic holy books are the records which most Muslims believe were dictated by
God to various prophets.
Muslims believe that parts of the previously revealed scriptures, the
Tawrat (
Torah) and the
Injil (
Gospels), had become
distorted—either in interpretation, in text, or both.
[56] The Quran (literally, "Reading" or "Recitation") is viewed by Muslims as the final revelation and literal word of God and is widely regarded as the finest
literary work in the
Arabic language.
[57][58]
Muslims believe that the verses of the Quran were revealed to
Muhammad by God through the
archangel Gabriel (
Jibrīl) on many occasions between 610 CE until his death on June 8, 632.
[59] While Muhammad was alive, all of these revelations were written down by his companions (
sahabah), although the prime method of transmission was orally through
memorization.
[60]
The Quran is divided into 114
suras, or chapters, which combined, contain 6,236
āyāt, or verses. The chronologically earlier suras, revealed at
Mecca, are primarily concerned with ethical and spiritual topics. The later
Medinan suras mostly discuss social and moral issues relevant to the Muslim community.
[61]
The Quran is more concerned with moral guidance than legal instruction, and is considered the "sourcebook of Islamic principles and values".
[62] Muslim jurists consult the
hadith ("reports"), or the written record of Prophet Muhammad's life, to both supplement the Quran and assist with its interpretation. The science of Quranic commentary and exegesis is known as
tafsir.
[63] The set of rules governing proper pronunciation is called
tajwid.
Muslims usually view "the Quran" as the original scripture as revealed in Arabic and that any translations are necessarily deficient, which are regarded only as commentaries on the Quran.
[64]
Prophets and sunnah

The Arabic word for prophets preceded by the honorific "peace be upon them".
Muslims identify the prophets of Islam (
Arabic:
أنۢبياء
anbiyāʾ ) as those humans chosen by God to be his messengers. According to the Quran, the prophets were instructed by God to bring the "will of God" to the peoples of the nations. Muslims believe that prophets are human and not divine, though some are able to perform miracles to prove their claim.
Islamic theology says that all of God's messengers preached the message of Islam—submission to the will of God. The Quran mentions the names of numerous figures considered
prophets in Islam, including
Adam,
Noah,
Abraham,
Moses and
Jesus, among others.
[65]
Muslims believe that God finally sent Muhammad as the last law bearing prophet (
Seal of the Prophets) to convey the divine message to the whole world (to sum up and to finalize the word of God). In Islam, the "normative" example of Muhammad's life is called the
Sunnah (literally "trodden path"). Muslims are encouraged to emulate Muhammad's actions in their daily lives and the Sunnah is seen as crucial to guiding interpretation of the Quran.
[66] This example is preserved in traditions known as hadith, which recount his words, his actions, and his personal characteristics. Hadith Qudsi is a sub-category of hadith, regarded as verbatim words of God quoted by Muhammad but is not part of the Quran.
A hadith involves two elements- a chain of narrators, called
sanad, and the actual wording, called
matn. Hadiths can be classified, by studying the narration, as "authentic" or "correct", called
Sahih (
Arabic:
صَحِيْح), "good", called
Ḥasan (
Arabic:
حَسَن) or "weak", called
Ḍaʻīf (
Arabic:
ضَعِيْف) among others.
Muhammad al-Bukhari[67] collected over 300,000 hadith, but only included 2,602 distinct hadith that passed the tests that codified them as authentic into his book
Sahih al-Bukhari,
[67] which is considered by many to be the most
authentic source after the Quran.
[68][69]
Resurrection and judgment
Belief in the "Day of Resurrection",
Yawm al-Qiyāmah (
Arabic:
يوم القيامة) is also crucial for Muslims. They believe the time of
Qiyāmah is preordained by God but unknown to man. The trials and
tribulations preceding and during the
Qiyāmah are described in the Quran and the hadith, and also in the commentaries of
scholars. The Quran emphasizes
bodily resurrection, a break from the
pre-Islamic Arabian understanding of death.
[70]
On Yawm al-Qiyāmah, Muslims believe all mankind will be judged on their good and bad deeds and consigned to
Jannah (paradise) or
Jahannam (hell). The Qurʼan in Surat al-Zalzalah describes this as, "So whoever does an atom's weight of good will see it (99:7) and whoever does an atom's weight of evil will see it (99:8)." The Qurʼan
lists several sins that can condemn a person to
hell, such as
disbelief in God (
Arabic:
كفر
kufr), and dishonesty; however, the Qurʼan makes it clear God will forgive the
sins of those who repent if he so wills. Good deeds, such as charity, prayer and compassion towards animals,
[71][72] will be rewarded with entry to heaven. Muslims view
heaven as a place of joy and bliss, with Qurʼanic references describing its features and the physical pleasures to come. Mystical traditions in Islam place these heavenly delights in the context of an ecstatic awareness of God.
[73]
Yawm al-Qiyāmah is also identified in the Quran as
Yawm ad-Dīn (
Arabic:
يوم الدين), "Day of Religion";
[74] as-sāʿah (
Arabic:
الساعة), "the Last Hour";
[75] and
al-Qāriʿah (
Arabic:
القارعة), "The Clatterer".
[76]
Divine will
The concept of divine will is referred to as
al-qadā wa'l-qadar (
Arabic:
قدر), which literally derives from a root that means
to measure. Everything, good and bad, is believed to have been decreed.
[77]
Acts of worship
There are five basic religious acts in Islam, collectively known as 'The Pillars of Islam' (
arkan al-Islam; also
arkan ad-din, "pillars of religion"), which are considered obligatory for all believers. The Quran presents them as a framework for worship and a sign of commitment to the faith. They are (1) the creed (
shahadah), (2) daily prayers (
salat), (3) almsgiving (
zakah), (4) fasting during
Ramadan, and (5) the pilgrimage to Mecca (
hajj) at least once in a lifetime.
[78] Both
Shia and
Sunni sects agree on the essential details for the performance of these acts.
[79] Apart from these, Muslims also perform other religious acts. Notable among them are charity (
Sadaqah) and
recitation of the Quran.
Testimony
The
Shahadah,
[80] which is the basic
creed of Islam that must be recited under
oath with the specific statement: "
'ašhadu 'al-lā ilāha illā-llāhu wa 'ašhadu 'anna muħammadan rasūlu-llāh", or "I testify that there is no god but
God, Muhammad is the messenger of God."
[81] This testament is a foundation for all other beliefs and practices in Islam. Muslims must repeat the
shahadah in prayer, and non-Muslims wishing to
convert to Islam are required to recite the creed.
[82]
Prayer
Ritual prayers are called Ṣalāh or Ṣalāt (
Arabic:
صلاة). Salat is intended to focus the mind on
God, and is seen as a personal communication with him that expresses gratitude and
worship. Performing prayers five times a
day is compulsory but flexibility in the specifics is allowed depending on circumstances. The prayers are recited in the
Arabic language, and consist of verses from the Quran.
[83] The prayers are done with the chest in direction of the
kaaba though in the early days of Islam, they were done in direction of
Jerusalem. The act of supplicating is referred to as
dua.
A mosque is a
place of worship for Muslims, who often refer to it by its Arabic name
masjid. A large mosque for gathering for Friday prayers or Eid prayers are called
masjid jāmi.
[84] Although the primary purpose of the mosque is to serve as a place of prayer, it is also important to the
Muslim community as a place to meet and study. In Medina,
Al-Masjid al-Nabawi, or the Prophet's Mosque, was also a place of refuge for the poor.
[85] Modern mosques have evolved greatly from the early designs of the 7th century, and contain a variety of architectural elements such as
minarets.
[86]
Charity
"Zakāt" (
Arabic:
زكاة
zakāh "
alms") is giving a fixed portion of accumulated wealth by those who can afford it to help the poor or needy and for those employed to collect Zakat; also, for bringing hearts together, freeing captives, for those in debt (or
bonded labour) and for the (stranded) traveller.
[87][88] It is considered a religious obligation (as opposed to voluntary charity) that the well-off owe to the needy because their wealth is seen as a "trust from God's bounty". Conservative estimates of annual zakat is estimated to be 15 times global humanitarian aid contributions.
[89] The amount of zakat to be paid on
capital assets (e.g. money) is 2.5% (1/40) per year,
[90] for people who are not poor.
Sadaqah means optional charity which is practiced as religious duty and out of generosity.
[91] Both the Quran and the hadith have put much emphasis on spending money for the welfare of needy people,
[92] and have urged the Muslims to give more as an act of optional charity.
[93] The Quran says: Spend something (in charity) out of the substance which We have bestowed on you, before Death should come to any of you (
63:10). One of the early teachings of Muhammad was that
God expects men to be generous with their wealth and not to be miserly (Quran
:1 107 :1–7).
[94] Accumulating wealth without spending them to address the needs of the poor is generally prohibited and admonished.
[95] Another kind of charity in Islam is
waqf which means perpetual religious endowment.
Fasting
Fasting (
Arabic:
صوم
ṣawm) from food and drink, among other things, must be performed from dawn to dusk during the month of
Ramadan. The fast is to encourage a feeling of nearness to God, and during it Muslims should express their gratitude for and dependence on him, atone for their past sins, and think of the needy.
Sawm is not obligatory for several groups for whom it would constitute an undue burden. For others, flexibility is allowed depending on circumstances, but missed fasts usually must be made up quickly.
[96]
Pilgrimage
The obligatory Islamic
pilgrimage, called the
ḥajj (
Arabic:
حج), has to be performed during the
Islamic month of
Dhu al-Hijjah in the city of Mecca. Every
able-bodied Muslim who can afford it must make the pilgrimage to Mecca at least once in his or her lifetime. Rituals of the Hajj include: spending a day and a night in the tents in the desert plain of Mina, then a day in the desert plain of Arafat praying and worshiping God, following the foot steps of Abraham; then spending a night out in the open, sleeping on the desert sand in the desert plain of Muzdalifah; then moving to Jamarat, symbolically
stoning the Devil recounting Abraham's actions;
[97][98][99] then going to Mecca and walking seven times around the
Kaaba which Muslims believe was built as a place of worship by Abraham; then walking seven times between
Mount Safa and
Mount Marwah recounting the steps of Abraham's wife, while she was looking for water for her son Ismael in the desert before Mecca developed into a settlement.
[100] Another form of pilgrimage,
Umrah, can be undertaken at any time of the year.
Recitation and memorization of the Quran
Muslims recite and memorize the whole or the part of the Quran as acts of virtue.
Reciting the Quran in the correct manner has been described as an excellent act of worship.
[101] Pious Muslims recite the whole Quran at the month of
Ramadan.
[102] In Islamic societies, any social program generally begins with the recitation of the Quran.
[102] Those who memorize the whole Quran is called
hafiz who, it is said, will be able to intercede for ten people on the Last Judgment Day.
[101] Apart from this, almost every Muslim memorizes some portion of the Quran because they need to recite it during regular prayer.
Society
Family life
For Muslim communities, family is the basic component of society, and is responsible for the wellbeing of its members. In a Muslim family, the birth of a child is attended with some religious ceremonies. Immediately after the birth, the words of
Adhan is pronounced in the right ear of the child. In the seventh day, the aquiqa ceremony is performed in which an animal is sacrificed and its meat is distributed among the poor.
[103] The head of the child is also shaved, and an amount of money equaling the weight of the child's hair is donated to the poor.
[103] Apart from fulfilling the basic needs of food, shelter, and education, the parents or the elderly members of family also undertake the task of teaching moral qualities, religious knowledge, and religious practices to the children.
[104] Marriage, which serves as the foundation of a Muslim family, is a civil contract which consists of an offer and acceptance between two qualified parties in the presence of two witnesses. The groom is required to pay a bridal gift (
mahr) to the bride, as stipulated in the contract.
[105] Most families in the Islamic world are monogamous.
[106][107] Polyandry, a form of
polygamy, where a woman takes on two or more husbands is prohibited in Islam.
[108] With Muslims coming from diverse backgrounds including 49 Muslim-majority countries, plus a strong presence as large minorities throughout the world there are many variations on Muslim Weddings. Generally in a Muslim family, a woman's sphere of operation is the home and a man's corresponding sphere is the outside world. However, in practice, this separation is not as rigid as it appears.
[109]
Certain religious rites are performed during and after the
death of a Muslim. Those near a dying man encourage him to pronounce the
Shahada as Muslims want their last word to be their profession of faith. After the death, the body is bathed properly by the members of the same gender and then enshrouded in a threefold white garment called
kafan.
[110] Placing the body on a
bier, it is first taken to a mosque where funeral prayer is offered for the dead person, and then to the graveyard for burial.
Etiquette and diet
Many practices fall in the category of
adab, or Islamic etiquette. This includes greeting others with "
as-salamu `alaykum" ("peace be unto you"), saying
bismillah ("in
the name of God") before meals, and using only the right hand for eating and drinking.
Islamic hygienic practices mainly fall into the category of personal cleanliness and health.
Circumcision of male offspring is also practiced in Islam.
Islamic burial rituals include saying the
Salat al-Janazah ("funeral prayer") over the bathed and enshrouded dead body, and burying it in a
grave. Muslims are restricted in their diet. Prohibited foods include pork products, blood,
carrion, and
alcohol. All meat must come from a
herbivorous animal slaughtered in the name of God by a Muslim, Jew, or Christian, with the exception of game that one has hunted or fished for oneself. Food permissible for Muslims is known as
halal food.
[111]
Social responsibilities
In a Muslim society, various social service activities are performed by the members of the community. As these activities are instructed by
Islamic canonical texts, a Muslim's religious life is seen incomplete if not attended by service to humanity.
[112] In fact, In Islamic tradition, the idea of social welfare has been presented as one of its principal values.
[112] The
2:177 verse of the Quran is often cited to encapsulate the Islamic idea of social welfare.
[113] Similarly, duties to parents, neighbors, relatives, sick people, the old, and the
minority have been defined in Islam. Respecting and obeying one's
parents, and taking care of them especially in their old age have been made a religious obligation.
[104][114] A two-fold approach is generally prescribed with regard to the duties to the
relatives: keeping rood relation with them, and offering financial help if necessary.
[115] Severing ties with them has been admonished. Regardless of a neighbor's religious identity, Islam tells the Muslims to treat their
neighboring people in the best possible manners and not to cause any difficulty to them.
[116][117] About the
orphaned children, the Quran forbids harsh and oppressive treatment to them while urging kindness and justice towards them. It also rebukes those who do not honor and feed the orphaned children (Quran
89:17-18).
Moral behavior
The Quran and the
sunnah of Muhammad prescribe a comprehensive body of moral guidelines for Muslims to be followed in their personal, social, political, and religious life. Proper moral conduct, good deeds, righteousness, and
good character come within the sphere of the moral guidelines.
[118] In Islam, the observance of moral virtues is always associated with religious significance because it elevates the religious status of a
believer[119] and is often seen as a supererogatory act of worshipping.
[120] One typical Islamic teaching on
morality is that imposing a penalty on an offender in proportion to their offense is permissible and just; but forgiving the offender is better. To go one step further by offering a favor to the offender is regarded the highest excellence.
[119] The Quran says: 'Repel (evil) with what is best' (
41:34). Thus, a Muslim is expected to act only in good manners as bad manners and deeds earn vices.
[121] The fundamental moral qualities in Islam are
justice,
forgiveness, righteousness, kindness, honesty, and piety.
[118] Other mostly insisted moral virtues include but not limited to charitable activities, tolerance, fulfillment of promise,
modesty and
humility, decency in speech, trustworthiness,
patience, truthfulness,
anger management, and sincerity of intention.
As a religion, Islam emphasizes the idea of having a good character as Muhammad said: 'The best among you are those who have the best manners and character' (
Sahih al-Bukhari,
8:73:56). In Islam, justice is not only a moral virtue but also an obligation to be fulfilled under all circumstances.
[122] The Quran and the hadith describe God as being kind and merciful to His creatures, and tell people to be kind likewise. As a virtue, forgiveness is much celebrated in Islam, and is regarded as an important Muslim practice.
[123] About modesty, Muhammad is reported as saying: ' Every religion has its characteristic, and the characteristic of Islam is modesty'.
[124]
Government
Mainstream Islamic law does not distinguish between "matters of church" and "matters of state"; the
scholars function as both jurists and theologians. Currently no government conforms to
Islamic economic jurisprudence, but steps have been taken to implement some of its tenets.
[125][126][127]
Law and jurisprudence

Men reading the Quran in
Mosque
The
Shariʻah (literally "the path leading to the watering place") is Islamic law and constitutes a system of duties that are incumbent upon a Muslim by virtue of his or her religious belief.
[128] The study of Islamic law is called
Fiqh, or "Islamic jurisprudence". The methods of jurisprudence used are known as
usul al-fiqh ("legal theory", or "principles of jurisprudence"). Much of it has evolved with the objective to prevent innovation or alteration in the original religion, known as
bid‘ah. Four fundamental evidence, codified by
ash-Shafi'i, used are, in order of precedence: the Quran, the Hadith (the practice of Muhammad), the consensus of the Muslim jurists (
ijma), and analogical reasoning (
qiyas). Rulings over actions can be categorized as those that are obligatory (
fardh) recommendanded (
mustahabb), permissible (
mubah), not recommended (
makrooh) and prohibited (
haraam).
The Quran set the rights, the responsibilities and the rules for people and for societies to adhere to. Muhammad provided an example, which is recorded in the hadith books, showing how he practically implemented those rules in a society.
Many of the Sharia laws that differ are devised through
Ijtihad where there is no such ruling in the Quran or the Hadiths of
Islamic prophet Muhammad regarding a similar case.
[129][130] As Muhammad's companions went to new areas,
[131] they were pragmatic and in some cases continued to use the same ruling as was given in that area during pre-Islamic times. If the population felt comfortable with it, it was just and they used Ijtihad to deduce that it did not conflict with the Quran or the Hadith. This made it easier for the different communities to integrate into the Islamic State and that assisted in the quick expansion of the Islamic State.
Islamic law covers all aspects of life, from matters of state, like governance and
foreign relations, to issues of daily living. The Quran defines
hudud as the punishments for five specific crimes: unlawful intercourse, false accusation of unlawful intercourse, consumption of alcohol, theft, and highway robbery. The Quran and Sunnah also contain laws of
inheritance,
marriage, and restitution for injuries and murder, as well as rules for
fasting,
charity, and prayer. For example, the division of
inheritance is specified in the Quran, which states that most of it is to pass to the immediate family, while a portion is set aside for the payment of debts and the making of bequests. The woman's share of inheritance is generally half of that of a man with the same rights of succession.
[132]
Scholars
Islam, like Judaism, has no
clergy in the
sacerdotal sense, such as priests who mediate between God and people. However, there are many terms in Islam to refer to religiously sanctioned positions of Islam. In the broadest sense, the term
ulema (
Arabic:
علماء) is used to describe the body of Muslim scholars who have completed several years of training and study of
Islamic sciences. A jurist who interprets Islamic law is called a
mufti (
Arabic:
مفتي) and often issues judicial opinions, called
fatwas. A scholar of jurisprudence is called a
faqih (
Arabic:
فقيه). Someone who studies the science of hadith is called a
muhaddith. A
qadi is a judge in an Islamic court.
Honorific titles given to scholars include
shiekh,
mullah and
maulvi.
Imam (
Arabic:
إمام) is a leadership position, often used in the context of conducting Islamic worship services.
Schools of jurisprudence

The main Islamic
madh'habs (schools of law) of Muslim countries or distributions
A school of jurisprudence is referred to as a
madhab (
Arabic:
مذهب). The four major Sunni schools are the
Hanafi,
Maliki,
Shafi'i,
Hanbali and sometimes
Ẓāhirī while the two major Shia schools are
Ja'fari and
Zaidi. Each differ in their methodology, called
Usul al-fiqh. The following of decisions by a religious expert without necessarily examining the decision's reasoning is called
taqlid. The term
ghair muqallid literally refers to those who do not use taqlid and by extension do not have a
madhab.
[133] The practice of an individual interpretating law with independent reasoning is called
ijtihad.
[134]
Economics
To reduce the gap between the rich and the poor,
Islamic economic jurisprudence encourages trade,
[135] discourages the hoarding of wealth and outlaws interest-bearing loans (
usury; the term is
riba in
Arabic).
[136][137] Therefore, wealth is taxed through
Zakat, but trade is not taxed.
Usury, which allows the rich to get richer without sharing in the risk, is forbidden in Islam. Profit sharing and venture capital where the lender is also exposed to risk is acceptable.
[138] Hoarding of food for speculation is also discouraged.
[139]
Grabbing other people's land is also prohibited. The prohibition of
usury has resulted in the development of
Islamic banking. During the time of Muhammad, any money that went to the state, was immediately used to help the poor. Then in 634,
Umar formally established the welfare state
Bayt al-mal. The
Bayt al-mal or the welfare state was for the Muslim and Non-Muslim poor, needy, elderly, orphans, widows, and the disabled. The
Bayt al-mal ran for hundreds of years under the
Rashidun Caliphate in the 7th century and continued through the
Umayyad period and well into the
Abbasid era. Umar also introduced Child Benefit and Pensions for the children and the elderly.
[140][141][142][143]
Jihad
Jihad means "to strive or struggle" (in the way of God). Jihad, in its broadest sense, is "exerting one's utmost power, efforts, endeavors, or ability in contending with an object of
disapprobation". Depending on the object being a visible enemy, the
Devil, and aspects of one's own self (such as sinful desires), different categories of jihad are defined.
[144] Jihad, when used without any qualifier, is understood in its military aspect.
[145][146] Jihad also refers to one's striving to attain religious and moral perfection.
[147] Some Muslim authorities, especially among the Shi'a and
Sufis, distinguish between the "greater jihad", which pertains to spiritual
self-perfection, and the "lesser jihad", defined as warfare.
[148]
Within
Islamic jurisprudence, jihad is usually taken to mean military exertion against non-believer/non-Muslim/Muslim combatants. The ultimate purpose of military jihad is debated, both within the Islamic community and without. Jihad is the only form of warfare permissible in Islamic law and may be declared against illegal works, terrorists, criminal groups, rebels,
apostates, and leaders or states who oppress Muslims.
[149][150]Most Muslims today interpret Jihad as only a defensive form of warfare.
[151] Jihad only becomes an individual duty for those vested with authority. For the rest of the populace, this happens only in the case of a
general mobilization.
[150] For most
Twelver Shias,
offensive jihad can only be declared by a
divinely appointed leader of the Muslim community, and as such is suspended since
Muhammad al-Mahdi's
[152] occultation in 868 AD.
[153]
History
A panoramic view of
Al-Masjid al-Nabawi (the Mosque of the Prophet) in
Medina,
Hejaz region, today's Saudi Arabia, the second most sacred Mosque in Islam
Muhammad (610–632)
Muslim tradition views Muhammad (c. 570 – June 8, 632) as the
seal of the prophets.
[154] During the last 22 years of his life, beginning at age 40 in 610
CE, according to the earliest surviving biographies, Muhammad reported revelations that he believed to be from God, conveyed to him through the
archangel Gabriel (
Jibril). Muhammad's
companions memorized and recorded the content of these revelations, known as the Quran.
[155]
During this time,
Muhammad in Mecca preached to the people, imploring them to abandon polytheism and to worship one God. Although some converted to Islam, the leading Meccan authorities persecuted Muhammad and his followers. This resulted in the
Migration to Abyssinia of some Muslims (to the
Aksumite Empire). Many early converts to Islam were the poor and former slaves like
Bilal ibn Rabah al-Habashi. The Meccan élite felt that Muhammad was destabilising their social order by preaching about one God and about racial equality, and that in the process he gave ideas to the poor and to their slaves.
[156][157][158][159]
The Constitution established:
- the security of the community
- religious freedoms
- the role of Medina as a sacred place (barring all violence and weapons)
- the security of women
- stable tribal relations within Medina
- a tax system for supporting the community in time of conflict
- parameters for exogenous political alliances
- a system for granting protection of individuals
- a judicial system for resolving disputes where non-Muslims could also use their own laws and have their own judges.[162][163][164]
All the tribes signed the agreement to defend Medina from all external threats and to live in harmony amongst themselves. Within a few years, two battles took place against the Meccan forces: first, the
Battle of Badr in 624 - a Muslim victory, and then a year later, when the Meccans returned to Medina, the
Battle of Uhud, which ended inconclusively.
The Arab tribes in the rest of Arabia then formed a confederation and during the
Battle of the Trench (March–April 627) besieged Medina, intent on finishing off Islam. In 628, the
Treaty of Hudaybiyyah was signed between Mecca and the Muslims and was broken by Mecca two years later. After the signing of the Treaty of Hudaybiyyah many more people converted to Islam. At the same time, Meccan trade routes were cut off as Muhammad brought surrounding desert tribes under his control.
[165] By 629 Muhammad was victorious in the nearly bloodless
conquest of Mecca, and by the time of his death in 632 (at the age of 62) he had united the
tribes of Arabia into a single religious
polity.
[166]
The earliest three generations of Muslims are known as the
Salaf, with the companions of Muhammad being known as the
Sahaba. Many of them, such as the largest narrator of hadith
Abu Hureyrah, recorded and compiled what would constitute the sunnah.
Caliphate and civil strife (632–750)
With Muhammad's death in 632, disagreement broke out over who would succeed him as leader of the Muslim community.
Abu Bakr, a companion and close friend of Muhammad, was made the first
caliph. Under
Abu Bakr put down a rebellion by Arab tribes in an episode known as the
Ridda wars, or "Wars of Apostasy".
[167] The Quran was compiled into a single volume at this time.
When Umar was assassinated by Persians in 644,
the election of Uthman as successor was met with increasing opposition. The standard copies of the Quran were also distributed throughout the Islamic State. In 656, Uthman was also killed, and Ali assumed the position of caliph. This led to the
first civil war (the "First Fitna") over who should be caliph. Ali was assassinated by
Kharijites in 661. To avoid further fighting, the new caliph
Hasan ibn Ali signed a
peace treaty, abdicating to
Mu'awiyah, beginning the
Umayyad dynasty, in return that he not name his own successor.
[170] These disputes over religious and political leadership would give rise to schism in the Muslim community. The majority accepted the legitimacy of the first four leaders, and became known as Sunnis. A minority disagreed, and believed that only Ali and some of his descendants should rule; they became known as the Shia.
[171] Mu'awiyah appointed his son,
Yazid I, as successor and after Mu'awiyah's death in 680, the "
Second Fitna" broke out, where
Husayn ibn Ali was killed at the
Battle of Karbala, a significant event in Shia Islam.
Classical era (750–1258)
During this time, the
Delhi Sultanate took over northern parts of Indian subcontinent. Religious missions converted
Volga Bulgaria to Islam. Many Muslims also went to
China to trade, virtually dominating the import and export industry of the
Song Dynasty.
[183]
Al-Shafi'i codified a method to determine the reliability of hadith.
[202] During the early Abbasid era, the major
Sunni hadith collections were compiled by scholars such as
Bukhari and
Muslim while major
Shia hadith collections by scholars such as
Al-Kulayni and
Ibn Babawayh were also compiled. The
Ja'fari jurisprudence was formed from the teachings of
Ja'far al-Sadiq while the four Sunni
Madh'habs, the
Hanafi,
Hanbali,
Maliki and
Shafi'i, were established around the teachings of
Abū Ḥanīfa,
Ahmad bin Hanbal,
Malik ibn Anas and
al-Shafi'i respectively. In the 9th century, al-Shafi'i provided a theoretical basis for Islamic law by codifying the principles of jurisprudence in his book
ar-Risālah.
[203] Al-Tabari and
Ibn Kathir completed the most commonly cited commentaries on the Quran, the
Tafsir al-Tabari in the 9th century and the
Tafsir ibn Kathir in the 14th century, respectively. Philosophers
Al-Farabi and
Avicenna sought to incorporate Greek principles into Islamic theology, while others like
Al-Ghazali argued against them and ultimately prevailed.
[204]
Caliphs such as
Mamun al Rashid and
Al-Mu'tasim made the
mutazilite philosophy an official creed and imposed it upon Muslims to follow. Mu'tazila was a Greek influenced school of speculative theology called
kalam, which refers to
dialectic.
[205] Many orthodox Muslims rejected
mutazilite doctrines and condemned their idea of the creation of the Quran. In inquisitions, Imam Hanbal refused to conform and was tortured and sent to an unlit
Baghdad prison cell for nearly thirty months.
[206] The other branch of kalam was the
Ash'ari school founded by
Al-Ash'ari.
Some Muslims began to question the piety of indulgence in a worldly life and emphasized poverty, humility and avoidance of
sin based on renunciation of bodily desires. Ascetics such as
Hasan al-Basri would inspire a movement that would evolve into Tasawwuf (Sufism).
[207] Beginning in the 13th century, Sufism underwent a transformation, largely because of efforts to legitimize and reorganize the movement by
Al-Ghazali, who developed the model of the
Sufi order—a community of spiritual teachers and students.
[208]
The first Muslims states independent of a unified Muslim state emerged from the Berber Revolt (739/740-743). In 930, the Ismaili group known as the
Qarmatians unsuccessfully rebelled against the Abbassids, sacked Mecca and stole the Black Stone, which was eventually retrieved.
[209] The
Mongol Empire put an end to the Abbassid dynasty in 1258.
[210]
Pre-Modern era (1258–20th century)
The majority and oldest group among Shia at that time, the
Zaydis, named after the great grandson of Ali, the scholar
Zayd ibn Ali, used the Hanafi jurisprudence, as did most Sunnis.
[220][221][222] The Shia
Safavid dynasty rose to power in 1501 and later conquered all of Iran.
[223] The ensuing mandatory
conversion of Iran to Twelver Shia Islam for the largely Sunni population also ensured the final dominance of the Twelver sect within Shiism over the
Zaidi and
Ismaili sects.
[224] Nader Shah, who overthrew the Safavids, attempted to improve relations with Sunnis by propagating the integration of Shiism by calling it the Jaafari Madh'hab.
[225]
Modern times (20th century–present)
Contact with industrialized nations brought Muslim populations to new areas through economic migration. Many Muslims migrated as indentured servants, from mostly India and
Indonesia, to the
Caribbean, forming the largest Muslim populations by percentage in the
Americas.
[228] The resulting urbanization and increase in trade in
sub-Saharan Africa brought Muslims to settle in new areas and spread their faith, likely doubling its Muslim population between 1869 and 1914.
[229] Muslim immigrants began arriving, many as
guest workers and largely from former colonies, in several Western European nations since the 1960s.
There are more and more new Muslim intellectuals who increasingly separate perennial Islamic beliefs from archaic cultural traditions.
[230] Liberal Islam is a movement that attempts to reconcile religious tradition with modern norms of secular governance and
human rights. Its supporters say that there are multiple ways to read Islam's sacred texts, and they stress the need to leave room for "independent thought on religious matters".
[231] Women's issues receive significant weight in the modern discourse on Islam.
[232]
Secular powers such as the Chinese
Red Guards closed many mosques and destroyed Qurans,
[233] and
Communist Albania became the first country to ban the practice of every religion.
[234] About half a million Muslims were killed in
Cambodia by communists who, it is argued, viewed them as their primary enemy and wished to exterminate them since they stood out and worshipped their own god.
[235] In
Turkey, the military carried out coups to oust Islamist governments, and headscarves were banned in official buildings, as also happened in
Tunisia.
[236][237]
Piety appears to be deepening worldwide.
[243][244][245] In many places, the prevalence of the
hijab is growing increasingly common
[246] and the percentage of Muslims favoring Sharia laws has increased.
[247] With religious guidance increasingly available electronically, Muslims are able to access views that are strict enough for them rather than rely on state clerics who are often seen as stooges.
[244]
It is estimated that, by 2050, the number of Muslims will nearly equal the number of Christians around the world, “driven primarily by differences in fertility rates and the size of youth populations among the world’s major religions, as well as by people switching faiths.”
[248] Perhaps as a sign of these changes, most experts agree that Islam is growing faster than any other faith in
East and
West Africa.
[249][250]
Denominations
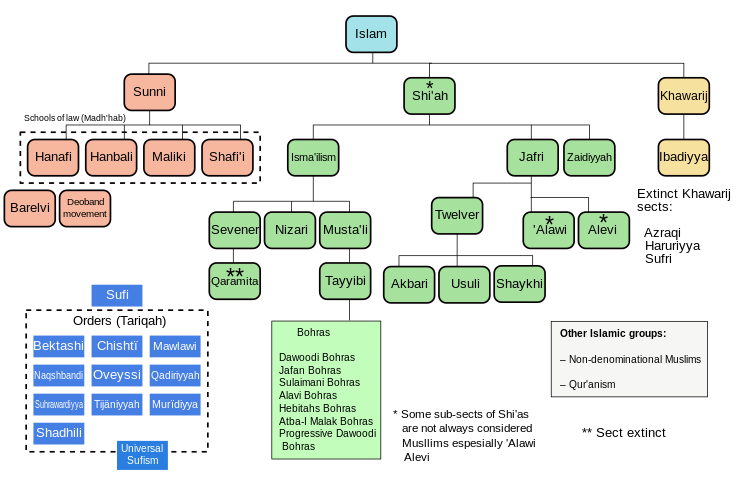
An overview of the major schools and branches of Islam.
Sunni
The largest denomination in Islam is Sunni Islam, which makes up 75%–90% of all Muslims
[27] and is arguably the world's largest religious denomination.
[251] Sunni Muslims also go by the name
Ahl as-Sunnah which means "people of the tradition [of Muhammad]".
[3][252][253][254][255] These hadiths, recounting Muhammad's words, actions, and personal characteristics, are preserved in traditions known as
Al-Kutub Al-Sittah (six major books).
Sunnis believe that the first four
caliphs were the rightful successors to Muhammad; since God did not specify any particular leaders to succeed him and those leaders were elected. Sunnis believe that anyone who is righteous and just could be a caliph but they have to act according to the Quran and the Hadith, the example of Muhammad and give the people their rights.
The Sunnis follow the Quran, then the Hadith. Then for legal matters not found in the Quran or the Hadith, they follow four
madh'habs (schools of thought):
Hanafi,
Hanbali,
Maliki and
Shafi'i, established around the teachings of
Abū Ḥanīfa,
Ahmad bin Hanbal,
Malik ibn Anas and
al-Shafi'i respectively. All four accept the validity of the others and a Muslim may choose any one that he or she finds agreeable.
[256] Ahl al-Hadith is a movement that deemphasized sources of jurisprudence outside the quran and sunnah, such as informed opinion (ra'y).
The
Barelvi movement, a revivalist movement of
Sunni Islam with over 200 million followers,
[258] emerged as part of debate of how to redeem India from the British. The movement emphasizes primacy of Islamic law in all matters with adherence to
Sufi practices and personal devotion to
Muhammad and has addressed leading issues for Muslims since partition.
[259][260] The
Deobandi movement is an Indo-Pakistani reformist movement that is much influenced by the Wahhabi movement.
[261] The Barelvi and Deobandi movements of
Sunni Islam accept the validity of all four Sunni madh'habs.
[262]
Shia
The Shia constitute 10–20% of Islam and are its second-largest branch.
[28]
Shia Islam has several branches, the most prominent being the
Twelvers (the largest branch),
Zaidis and
Ismailis. Different branches accept different descendants of Ali as Imams. After the death of Imam
Jafar al-Sadiq who is considered the sixth Imam by the
Twelvers and the
Ismaili's, the Ismailis recognized his son Isma'il ibn Jafar as his successor whereas the Twelver Shia's (Ithna Asheri) followed his other son
Musa al-Kadhim as the seventh Imam. The
Zaydis consider
Zayd ibn Ali, the uncle of Imam
Jafar al-Sadiq, as their fifth Imam, and follow a different line of succession after him.
Other smaller groups include the
Bohra as well as the
Alawites and
Alevi.
[266] Some Shia branches label other Shia branches that do not agree with their doctrine as
Ghulat.
Sufism
Sufism enjoyed a strong revival in central Asia and South Asia. Central Asia is considered to be a center of Sufism. Sufism has played a significant role in fighting against Tsars of Russia and Soviet colonization. Here, Sufis and their different orders are the main religious sources.
[274][275] Sufism is also strong in African countries such as
Tunisia,
Algeria,
Morocco,
Senegal,
Chad and
Niger.
[276][277]
Sufi practices such as veneration of saints have faced stiff opposition from followers of
Salafism and
Wahhabism, who have sometimes physically attacked Sufi places of worship, leading to deterioration in
Sufi–Salafi relations.
Other denominations
- Ahmadiyya is an Islamic reform movement (with Sunni roots) founded by Mirza Ghulam Ahmad[278] that began in India in 1889 and is practiced by 10 to 20 million[279] Muslims around the world. Ahmad claimed to have fulfilled the prophecies concerning the arrival of the 'Imam Mahdi' and the 'Promised Messiah'.
- The Ibadi is a sect that dates back to the early days of Islam and is a branch of Kharijite and is practiced by 1.45 million Muslims around the world.[280] Unlike most Kharijite groups, Ibadism does not regard sinful Muslims as unbelievers.
- Mahdavia is an Islamic sect that believes in a 15th-century Mahdi, Muhammad Jaunpuri
- The Quranists are Muslims who generally reject the Hadith.
- Yazdânism is seen as a blend of local Kurdish beliefs and Islamic Sufi doctrine introduced to Kurdistan by Sheikh Adi ibn Musafir in the 12th century.
- There are also black Muslim movements such as the Nation of Islam (NOI), Five-Percent Nation and Moorish scientists.
Non-denominational Muslims
Demographics
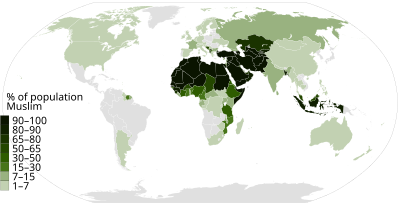
A comprehensive 2009 demographic study of 232 countries and territories reported that 23% of the global population, or 1.57 billion people, are Muslims. Of those, it is estimated that over 75–90% are
Sunni and 10–20% are
Shia[32][252][291] with a small minority belonging to other sects. Approximately 57 countries are
Muslim-majority,
[292] and
Arabs account for around 20% of all Muslims worldwide.
[293] The number of Muslims worldwide increased from 200 million in 1900 to 551 million in 1970,
[294] and tripled to 1.6 billion by 2010.
[248]
According to the
Pew Research Center, Islam is set to equal Christianity in number of adherents by the year 2050. Islam is set to grow faster than any other major world religion, reaching a total number of 2.76 billion (an increase of 73%). High fertility rates play a factor, with Islam having a rate of 3.1 compared to the world average of 2.5, and the minimum replacement level for a population at 2.1. Age also plays a role in these numbers due to the fact that Islam has the highest number of adherents under the age of 15 (34% of the total religion) of any major religion (Christianity's is 27%). Sixty percent of Muslims are between the ages of 16 and 59, while only 7% are aged 60+ (the smallest percentage of any major religion). Countries such as Nigeria and the Republic of Macedonia are expected to have Muslim majorities by 2050. In India, the Muslim population will be larger than any other country. Europe's domestic population is set to shrink as opposed to their Islamic population which is set to grow to 10% of Europe's total.
[248] According to BBC News, the rates of growth of
Islam in Europe reveal that the growing number of Muslims is due primarily to immigration and higher
birth rates.
[306]
Culture
The term "
Islamic culture" could be used to mean aspects of culture that pertain to the
religion, such as
festivals and dress code. It is also controversially used to denote the cultural aspects of traditionally
Muslim people.
[307] Finally, "Islamic civilization" may also refer to the aspects of the synthesized culture of the early Caliphates, including that of non-Muslims,
[308] sometimes referred to as "
Islamicate".
Architecture
Art
While not condemned in the Quran, making images of human beings and animals is frowned on in many Islamic cultures and connected with
laws against idolatry common to all Abrahamic religions, as 'Abdullaah ibn Mas'ood reported that Muhammad said, "Those who will be most severely punished by Allah on the Day of Resurrection will be the image-makers" (reported by al-Bukhaari, see al-Fath, 10/382). However this rule has been interpreted in different ways by different scholars and in different historical periods, and there are examples of paintings of both animals and humans in Mughal, Persian and Turkish art. The existence of this
aversion to creating images of animate beings has been used to explain the prevalence of calligraphy, tessellation and pattern as key aspects of Islamic artistic culture.
[312]
Calendar

The phases of the moon form the basis for the Islamic calendar.
Criticism
Criticism of Islam has existed since Islam's formative stages. Early criticism came from Christians authors, many of whom viewed Islam as a Christian
heresy or a form of idolatry and often explained it in apocalyptic terms.
[315] Later there appeared criticism from the
Muslim world itself, and also from
Jewish writers and from ecclesiastical Christians.
[316][317][318]
Objects of criticism include the morality of the life of Muhammad, the last law bearing prophet of Islam, both in his public and personal life,
[318][319] as seen in
medieval Christian views on Muhammad. Issues relating to the authenticity and morality of the Quran, the Islamic holy book, are also discussed by critics.
[320][321] Other criticisms focus on the question of
human rights in modern Islamic nations, and the treatment of women in Islamic law and practice.
[322][323] In wake of the recent
multiculturalism trend, Islam's influence on the ability of Muslim immigrants in the West to assimilate has been
criticized.
[324] In classical Islamic law, the penalty for
apostasy (leaving a religion) in Islam is death.
[325] However the
Quran does not stipulate that the penalty for apostasy should be death.
[325]
See also
 :
: